Understanding the Uses and Benefits of a 3-Way Cannula in Medical Procedures


The 3-way stopcock is an indispensable tool in medical settings, facilitating precise control over fluids and significantly enhancing patient care. This small yet pivotal device is typically crafted from transparent or translucent materials and features a rotating handle along with three distinct ports: 'I' for input, 'O' for output, and 'II' for the side port. Its design allows for efficient management of fluid flow, making it essential in various medical procedures and treatments. This blog explores the functionality, applications, and importance of the 3-way stopcock in healthcare settings.
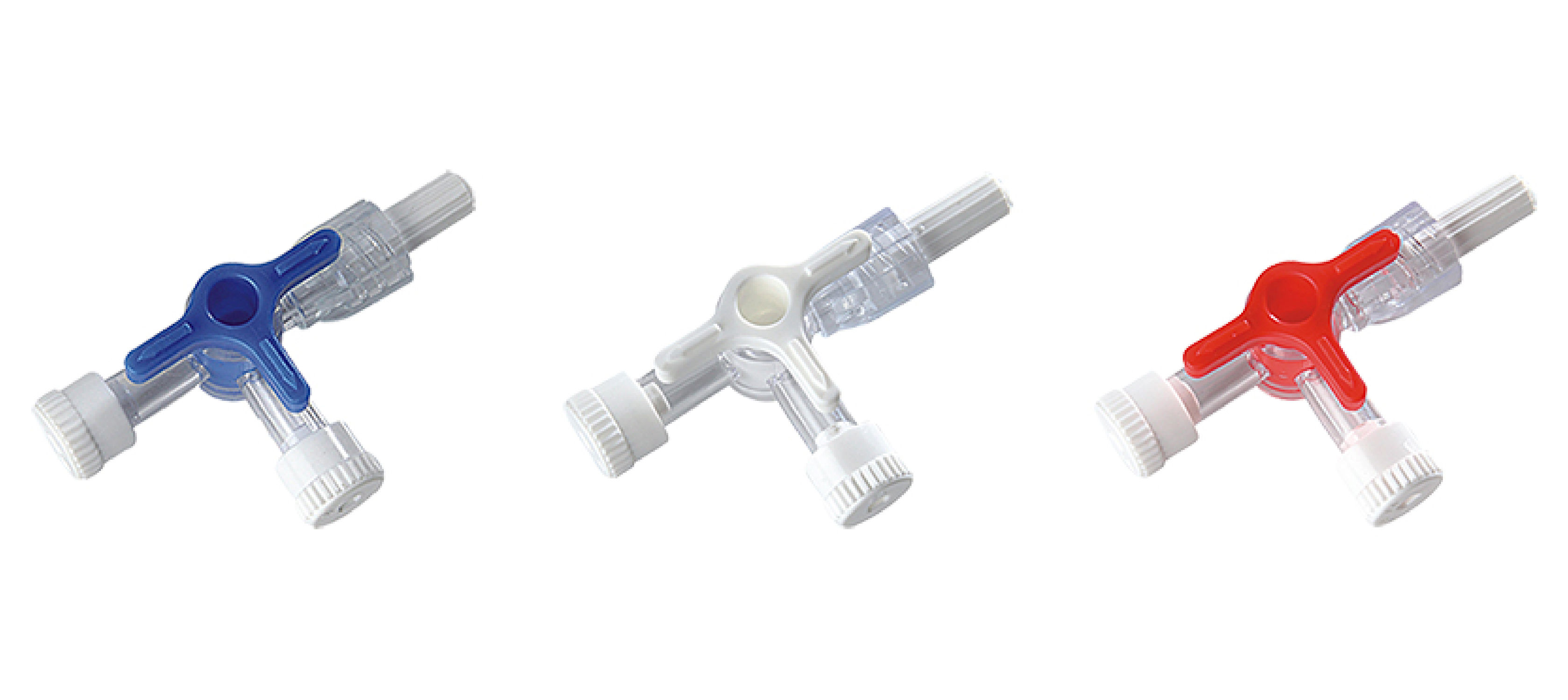
Anatomy of 3 Way Stop cock
Cannula Body:
Wings or Flanges:
Needle
Color-Coding
- Rotating Handle: The rotating handle is the central component of the 3-way stopcock, allowing healthcare professionals to manage the direction of fluid flow between the ports with precision.
- Colour Coding: Color coding for 3-way stopcocks helps healthcare providers quickly identify their specific functions or intended uses. Common color codes include:
Blue: Typically used for venous lines.
Red: Often designated for arterial lines.
White: Sometimes used for other specific applications or to indicate a different configuration.
- Input Port (I): The point where the fluid enters the stopcock.
- Output Port (O): The exit point for the fluid.
- Side Port (II): An additional opening for secondary connections or attaching monitoring devices.
How to Use a 3-Way IV Cannula
Following are the steps for using a 3-way Stopcock:
Step 1: Remove the stopcock from its packaging.
Step 2: Ensure the valve is in the closed position before use.
Step 3: Connect one or two IV lines to the female ports as needed.
Step 4: Remove the cap from the male port and connect the IV cannula securely.
Step 5: Open the tap to allow any air to escape.
Step 6: Adjust fluid flow by rotating the valve as required.
Step 7: Dispose of the stopcock safely after use.

What are the applications of 3-way stopcock in medical settings?
Intravenous (IV) Therapy: 3-way stopcocks play a vital role in IV therapy by facilitating the administration of multiple medications or fluids through a single access point. The rotating handle allows swift and controlled switching between different infusions, minimizing the need for multiple punctures.
Blood Transfusions: In blood transfusions, these devices enable healthcare professionals to seamlessly switch between various blood components, ensuring a smooth and continuous flow without requiring multiple setups.
Arterial Blood Gas Sampling: For arterial blood gas sampling, the side port of the 3-way stopcock connects to a syringe, simplifying the process of drawing arterial blood samples for analysis.
Benefits of 3-Way Stopcocks
Streamlined Fluid Management: The primary advantage lies in managing multiple fluid lines simultaneously. With three ports for connections, healthcare professionals can administer different medications or solutions without needing additional devices, simplifying the process and reducing contamination risks.
Real-Time Control and Adaptability: The rotating handle allows healthcare practitioners to swiftly adjust fluid flow, enabling instant adaptations during medical procedures. This control is critical in situations where precise fluid management is paramount.
Versatility in Medical Procedures: The versatility of 3-way stopcocks spans various medical procedures, including intravenous therapy and blood transfusions, enhancing the efficiency of medical professionals by offering a single solution for diverse fluid management needs.
Reduced Need for Additional Devices: By consolidating multiple functions into one device, 3-way stopcocks contribute to a more efficient and clutter-free medical environment, simplifying workflows and reducing the risk of complications from using multiple devices.
Enhanced Patient Safety: The precision and control offered by 3-way stopcocks directly enhance patient safety. Accurate fluid management minimizes medication errors and ensures timely treatment delivery, reducing complications from fluid mismanagement.
Cost-Effectiveness: Incorporating 3-way stopcocks into medical procedures can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for additional equipment and streamlining inventory management. Their versatility and durability make them a cost-effective solution for healthcare facilities.
Best Practices for Using 3-Way Stopcocks
Proper Priming: Ensure that the 3-way stopcock is properly primed to remove air bubbles, preventing air embolisms during fluid administration.
Labelling and Documentation: Clearly label the ports and document the connected medications or fluids to avoid confusion and enhance patient safety.
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect 3-way stopcocks for signs of damage or wear, replacing any devices that show signs of deterioration to maintain functionality and prevent leaks.
Training and Education: Healthcare professionals should receive proper training on the correct usage of 3-way stopcocks to maximize their benefits and minimize the risk of errors.
What to do when there are common complications and what can be the solutions?
Fluid Leakage and Cross-Contamination: Improper sealing or wear and tear can lead to fluid leakage, compromising procedure sterility and increasing contamination risks. Regular inspections and timely replacements can mitigate this.
Difficulty in Turning: Resistance in the rotating handle can impede smooth operation. Regular maintenance ensures the handle remains functional.
Incompatibility with Medications: Certain medications may degrade the valve components. Using high-quality, compatible materials can prevent this issue.
Blockage and Obstruction: Residual substances can block fluid pathways. Proper cleaning and maintenance prevent obstructions.
Sterility Breakdown: Ensuring the 3-way stopcock is adequately sterilized before use is crucial for maintaining sterility and preventing infections.
Misalignment of Ports: Correct alignment is essential for accurate fluid control. Regular checks ensure proper functionality.
Material Deterioration: Exposure to chemicals or repeated sterilization can degrade materials. Using durable materials and regular inspections prevent deterioration.
Limited Durability in High-Pressure Scenarios: High-pressure conditions can stress valve components. Selecting robust materials ensures longevity under such conditions.
The 3-way stopcock is vital in medical practice, it controls and provides help in fluid management. Its innovative design, comprising a rotating handle and three distinct ports, allows healthcare professionals to administer and manage multiple medications or fluids efficiently. This reduces the need for multiple access points, enhances patient safety, and streamlines medical procedures. As a result, 3-way stopcocks not only improve the efficiency of medical interventions but also significantly contribute to enhanced patient care and safety.
FAQs