Sphygmomanometer - Types, parts and working


A sphygmomanometer is an essential medical instrument used to measure blood pressure, helping in the diagnosis and monitoring of various health conditions. Understanding the different types of sphygmomanometers, recognizing the sphygmomanometer parts of the device, knowing how to use a sphygmomanometer correctly, and being aware of its various sphygmomanometer uses are crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals monitoring their health at home. This blog will guide you through all these aspects, providing a comprehensive overview of the sphygmomanometer and its role in healthcare.
What is Sphygmomanometer?
A sphygmomanometer is a device used to indirectly measure arterial blood pressure, a process known as sphygmomanometry. This method is commonly used in clinical settings to assess cardiovascular health.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
Often seen in doctors' offices and medical clinics, this type of sphygmomanometer is manually operated and widely used for accurate blood pressure readings.
Components:
· Inflatable Arm Cuff: Wraps around the arm to restrict blood flow during measurement.
· Bulb Pump and Valve: Used to inflate the cuff with air and control its release.
· Pressure Meter/Dial (Manometer): Measures the air pressure, often displayed alongside a column of mercury in traditional models.
Types of Sphygmomanometer:
There are three major types of Sphygmomanometer.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
The mercury sphygmomanometer or palm type sphygmomanometer is one of the most commonly used types for measuring blood pressure. It
features a graded tube filled with mercury that measures the pressure
exerted by the inflatable rubber cuff on the upper arm. For accurate
readings, the device is placed on a flat surface. While mercury
sphygmomanometers are known for their durability and long lifespan, their
use has been restricted or banned in some countries due to the toxic
nature of mercury.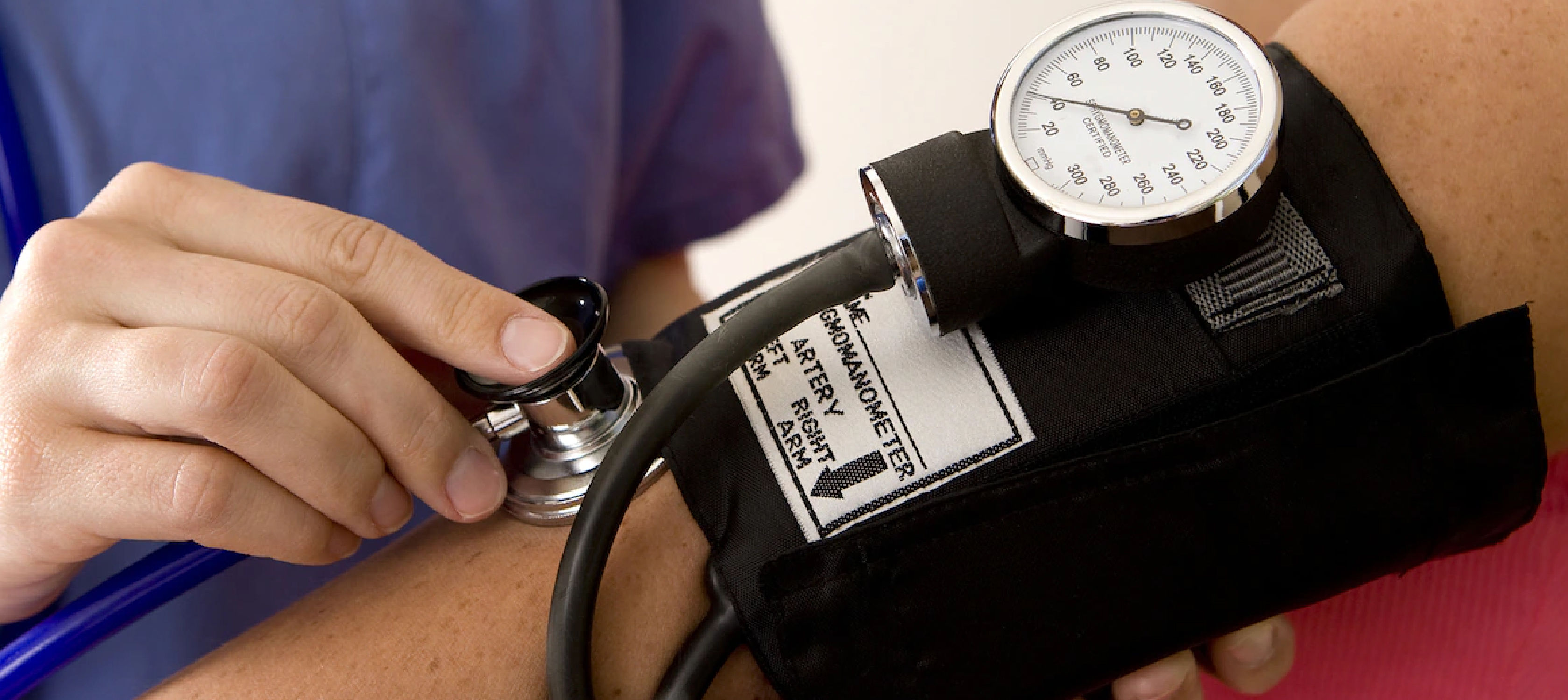
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
The aneroid sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure without the use of any fluid. In this type, the
stethoscope is directly attached to the cuff, which is connected to a
gauge with a dial. The dial gauge displays the pressure inside the cuff,
making it a portable and convenient option for both clinical and home
use.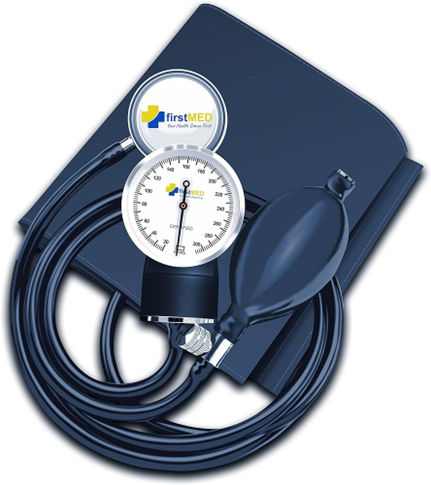
Automatic Digital Sphygmomanometer
The automatic digital sphygmomanometer electronically measures blood pressure by detecting arterial fluctuations. The cuff is directly connected to the device, and it inflates and deflates with the push of a button. Blood pressure readings are shown on a digital display.
Without any fluid, these devices are highly portable and convenient for
both home and clinical use.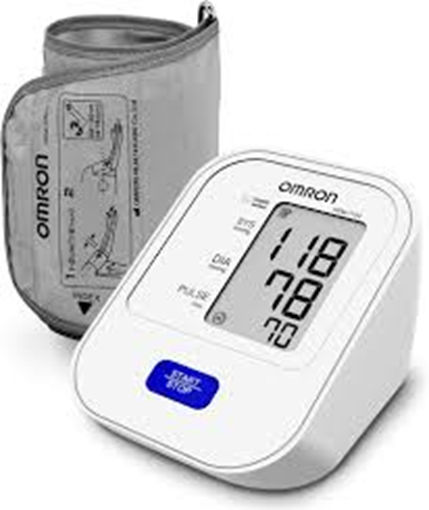
Parts of Sphygmomanometer:
A sphygmomanometer parts consists of three components:
Inflatable Rubber Cuff: Typically placed around the upper arm, this cuff can also be applied to other sphygmomanometer parts of the body in emergencies or specific situations.
Bladder: Located within the cuff, the bladder inflates as air is pumped into it, applying pressure to the arm.
Rubber Bulb: Connected to the bladder, the bulb is manually squeezed to inflate the
bladder with air. A valve located above the bulb allows for controlled
deflation of the bladder.
How to use a sphygmomanometer?
Using a sphygmomanometer involves different procedures depending on the type, but all types follow the same basic principle. The cuff is inflated using a bulb, and a valve is used to release the pressure gradually. During this process, a stethoscope is employed to listen to the sounds of arterial blood flow, which correspond to the systolic and diastolic pressure—key indicators of heart health.
Steps to Accurately Measure Blood Pressure:
· Blood pressure is recorded as systolic over diastolic pressure. A typical reading for a healthy adult is around 120/80 mmHg.
· Ensure the cuff is appropriately sized—about 80% of the upper arm's circumference. A cuff that is too loose or too tight can affect accuracy. Avoid placing the cuff over clothing.
· Wrap the cuff around the upper arm, keeping the lower edge about one inch above the antecubital fossa (the inside of the elbow).
· Place the stethoscope’s bell lightly over the brachial artery, just below the cuff’s lower edge.
· Use the bulb to inflate the cuff to 180 mmHg, then release the pressure slowly at a rate of about 3 mm per second.
· Watch the gauge or mercury column while listening for the first knocking sound through the stethoscope—this indicates the systolic pressure. The point where the sound disappears signifies the diastolic pressure.
· To ensure accuracy, measure the blood pressure on both arms. Note any differences in readings, as well as the patient's position and the cuff size used.
Sphygmomanometer Uses:
Following are the Sphygmomanometer Uses.
Measuring Blood Pressure: The primary use of a sphygmomanometer is to measure blood pressure in humans. It is also valuable in veterinary medicine, where it helps veterinarians diagnose and monitor blood pressure in animals.
Monitoring Medication Effectiveness: Doctors use sphygmomanometers to assess how well medications are working. The device provides two key readings: systolic (the upper number) and diastolic (the lower number), which help evaluate the impact of treatment on blood pressure.
Controlling Hypertension: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a serious condition that can lead to stroke, heart attack, or even death. Factors such as diabetes and smoking contribute to hypertension. Sphygmomanometers are essential for managing and controlling blood pressure, guiding both doctors and patients in taking necessary actions.
Detecting Diseases: High blood pressure can indicate underlying health issues. During medical check-ups, blood pressure readings from a sphygmomanometer help doctors detect potential illnesses and monitor ongoing health conditions.
First Aid in Emergencies: In emergency situations, sphygmomanometers are used to quickly assess patients' blood pressure. This information aids in delivering appropriate first aid and prioritizing treatment based on the severity of the condition and the extent of blood loss.
Research and Development: Organizations like the WHO use sphygmomanometers for medical research. They test new medications on animals such as rabbits, mice, or pigs, using blood pressure measurements to understand the effects of new drugs and predict their impact on humans.
In conclusion, the sphygmomanometer is a vital tool in both clinical and research settings, offering essential insights into blood pressure that are crucial for diagnosing and managing various health conditions. Whether used to monitor medication effectiveness, control hypertension, detect underlying diseases, provide emergency care, or facilitate medical research, this device plays a significant role in ensuring accurate and timely health assessments. Its applications extend beyond human medicine to veterinary care and research, highlighting its importance across multiple fields.
FAQs